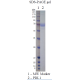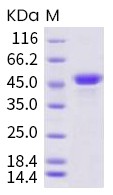
Recombinant Human CD40L
The human CD40L extracellular domain is consisted of amino acids 113-261 with an IgG-Fc tag at N-terminus. CD40L, also known as CD154 or TNFSF5, is a protein that is primarily expressed on the surface of activated CD4+ T cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily and is known to play an important role in immune system function, particularly in the regulation of B cell activation and differentiation. Dysregulation of CD40L signaling has been implicated in several autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, as well as in the development and progression of certain types of cancer. Targeting CD40L has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy in these conditions.